2.5 An overall architectural description should be produced to identify sub-systems
making up the system. Once these have been identified, they may be specified
in
parallel with other systems and the interfaces between sub-systems defined.
2.6 Exercise for the Student.
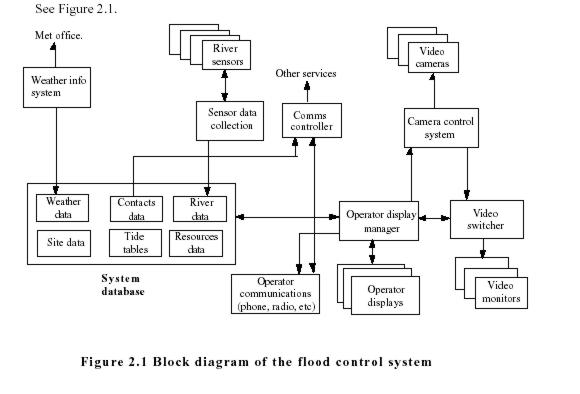
2.7 The key features of the solution are:
• Database with different types of data
• Video control system
• Operator console system
• River data collection
• Weather system links
• Communication control system
See Figure 2.1.
2.9 Arguments in favor of Systems Engineering as a discipline include, 1) it is an interdisciplinary profession consisting of specifying, designing, implementing, validating and maintaining the system as a whole. System engineers are concered with S/W and H/W and the system interactions with users and it's environment. Difficult to find a single system engineer that has the knowledge to satisfy the interdisciplinary requirements for the job.
3.1 (a) Anti-lock braking system Safety-critical system so method based on
formal
transformations with proofs of equivalence between each stage.
(b) Virtual reality system System whose requirements cannot be predicted in
advance
so exploratory programming model is appropriate.
(c) University accounting system System whose requirements should be stable
because of existing system therefore waterfall model is appropriate.
(d) Interactive timetable System with a complex user interface but which must
be
stable and reliable. Should be based on throw-away prototyping to find requirements
then either incremental development or waterfall model.
3.2 Programs developed using evolutionary development are difficult to maintain because